At Khandwala Eye Hospital You will be cared by an excellent Ophthalmologists for both your preoperative and postoperative visits. Here, Laser Vision Correction includes a pre-procedure visit and a thorough examination, the procedure itself, and all follow-up care to ensure the best possible results.
Understanding Squint..
Bringing your world in Focus..
Squint is a misalignment of the two eyes so that both the eyes are not looking in the same direction. This misalignment may be constant, being present throughout the day, or it may appear sometimes and the rest of the time the eyes may be straight.An eye with a squint may become unable to see clearly. This weak eye is called a lazy eye. Lazy eye can only be cured if detected and treated early. The earlier the treatment, the better the results. A person with a squint can only use one eye at a time. A person with two good eyes will be able to judge distances and depth more accurately than one with a squint. A squint may also affect the appearance and self-confidence of your child. Hence it is sometimes desirable to operate on the child’s squint at an early age. Hence it is sometimes desirable to operate on the child’s squint at an early age.
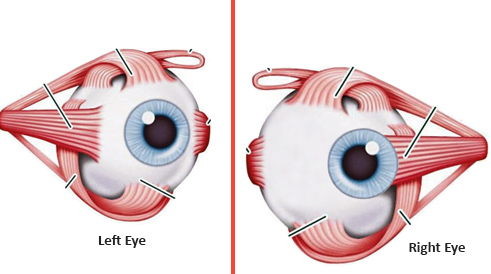
A condition of strabismus.
At K.E.H, Our unparalleled expertise and state-of-the-art equipment allow us to offer excellent medical and surgical treatment of the full range of routine, complex and high-risk corneal and external diseases.
What causes people to be cross eyed ?
 Strabismus ( Crossed Eye) can be caused by problems with the eye muscles, the nerves that transmit information to the muscles, or the control center in the brain that directs eye movements. It can also develop due to other general health conditions or eye injuries. Risk factors for developing strabismus include: Family history.
Strabismus ( Crossed Eye) can be caused by problems with the eye muscles, the nerves that transmit information to the muscles, or the control center in the brain that directs eye movements. It can also develop due to other general health conditions or eye injuries. Risk factors for developing strabismus include: Family history.
A Walkthough Video of Understanding Squint..
Early Detection and Treatment.
This is an important health issue. All children should have their first examination around 9 months of age. However, if an extreme or constant eye turn is noticed, the baby should be examined before 9 months. If a constant eye turn or significant refractive error is found, the eyes need to be fully evaluated and corrected as early as possible. A child with a squint needs a full eye checkup. Treatment may include a combination of patching, eye glasses, eye drops, eye exercises, and surgery. Treatment using the spectacles to correct any refractive errors may cure some types of squint, but to be effective the spectacles must be worn most of the time. As children often resist, the responsibility falls to the parents to make sure they wear their spectacles constantly. Any lazy eye must be treated.
How does a squint affect my child ?
The Lazy Eye :
An eye with a squint may become unable to see clearly. This weak eye is called a lazy eye. Lazy eye can only be cured if detected and treated early. The earlier the treatment, the better the results. A child with a squint can only use one eye at a time. A child with two good eyes will be able to judge distances and depth more accurately than one with a squint. This may affect the choice of your child’s future career and sports. A squint may also affect the appearance and self-confidence of your child. Hence it is sometimes desirable to operate on the child’s squint at an early age. Last, but not least, an eye with a squint may have other conditions which need treatment.For all these reasons, any infant or child with a squint should be examined by an eye specialist.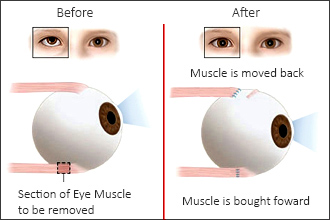
Squint Surgery:
Squint surgery is an operation on the muscles that move the eye. Strabismus surgery involves tightening the weak muscles and/or loosening the stronger ones so that the eyes are positioned better. Special absorbable stitches will hold the eye muscles in their new position. The surgeon will not cut the skin around the eye, take the eye out of its socket, or use any lasers during the operation. Sometimes both eyes need to be operated upon but this provides hardly any risk to the eye.Types of Squint Eyes..
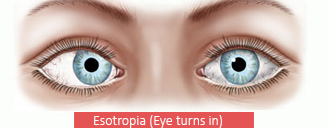
Esotropia's is a form of strabismus in which one or both eyes turns inward. The condition can be constantly present, or occur intermittently, and can give the affected individual a "cross-eyed" appearance. Esotropia is sometimes erroneously called “lazy eye,” which describes the condition of amblyopia—a reduction in vision of one or both eyes that is not the result of any pathology of the eye and cannot be resolved by the use of corrective lenses. Amblyopia can, however, arise as a result of esotropia occurring in childhood: In order to relieve symptoms of diplopia or double vision, the child's brain will ignore or “suppress” the image from the esotropic eye, which when allowed to continue untreated will lead to the development of amblyopia. Treatment options for esotropia include glasses to correct refractive errors.
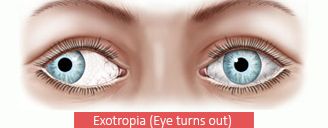 Exotropia is a form of strabismus (eye misalignment) in which one or both of the eyes turn outward. It is the opposite of crossed eyes, or esotropia. Exotropia may occur from time to time (intermittent exotropia) or may be constant, and is found in every age group. While it is possible for exotropia to become less frequent with age, most forms of exotropia do not resolve completely. However, some people may be able to adequately control the drifting with glasses or other non-surgical means. If the visual problem is treatable, it should be addressed as soon as possible.
Exotropia is a form of strabismus (eye misalignment) in which one or both of the eyes turn outward. It is the opposite of crossed eyes, or esotropia. Exotropia may occur from time to time (intermittent exotropia) or may be constant, and is found in every age group. While it is possible for exotropia to become less frequent with age, most forms of exotropia do not resolve completely. However, some people may be able to adequately control the drifting with glasses or other non-surgical means. If the visual problem is treatable, it should be addressed as soon as possible.
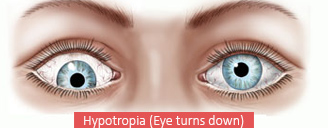
Hypotropia is the term used to describe the type of squint (abnormal alignment of the eyes) in which one eye - it can be either the right-eye, or the left-eye - looks downwards in situations in which one would usually expect both eyes to be directed other than downwards. Hypotropia can be treated with the following procedures: through corrective glasses, patching, prism therapy, surgical correction or botox injection. Surgical correction is the most ideal healthcare treatment of hypotropia. Surgery has the ability to bring binocularity, correct the cosmetic health defect and manage diplopia. However, surgical correction should only be used after thorough exam of a physician.